Office Hours
WE DON'T SLEEP......SO YOU CAN!
We Are Always Available.
24/7/365
Call For A Free Assessment
CALL NOW!
516-451-7876
Contact Us
IN THE NEWS
RESOURCES
TOP TEN MYTHS ABOUT BED BUGS: http://insects.about.com/od/HouseholdPests/a/Top-10-Myths-About-Bed-Bug-Treatment.htm
NEW YORK CITY BED BUG WEBSITE: http://www.nyc.gov/html/doh/bedbugs/html/home/home.shtml
Get Social With Us
Bed Bug Reproduction and Traumatic Insemination
Bed bugs reproduce in a way much different than other animals - even other insects. This process is very accurately called traumatic
insemination. Upon finding a female, the male locates a groove in the female's abdominal wall and stabs through her exoskeleton with his sexual organ. Once skewered, the male pumps in semen,
withdraws and crawls off to find another blood meal. Female bed bugs, after several
traumatic inseminations with males, often crawl off alone to recover. By crawling off to get some peace and quiet, she also winds up spreading the bed bug population throughout the general area. This
helps more bed bugs find more sources to feed from so that more and more and more bed bugs do not feed from the same body or bodies.
MOST INSEMINATED FEMALES ARE NOT IN COMMON
HARBORAGE AREAS DUE TO THIS PHENOMENON.
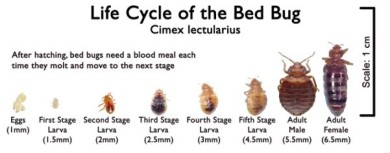
Bed Bug Biology
-
Bed bugs feed on the blood of human beings.
-
There are 5 nymph stages in a bed bug's lifecycle.
-
A bed bug will shed its skin after each stage in the lifecycle.
- A bed bug must partake in a blood meal to advance to
the next nymph stage. - After the 5th feeding, a bed bug is considered a fully grown adult.
- Nymphs become engorged with blood within three minutes, while adult bed bugs usually feed 10-15 minutes.
- From egg to adult, it takes between 30 and 50 days, depending on conditions.
- Bed bugs multiply rapidly and abundantly – females lay up to 5 eggs per day – making them one of the most stubborn pests to eradicate.
- A fully grown female bed bug can produce up to 300–500 eggs in its lifetime.
- Once the eggs are laid, it takes between 7–14 days for the eggs to hatch.
- A bed bug can survive without food for up to a year!
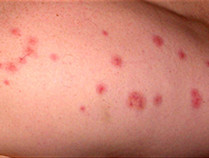
Bed Bug Bites
- Bed bugs pierce the skin with a sharp beak, then inject a salivary fluid containing an anti-coagulant and an anesthetic which helps them obtain blood.
- The salivary fluid of the bed bug causes varying reactions in their hosts, but are typically painless and result only in mild irritation and inflammation.
- Sensitivity to bed bugs varies so reactions may range from unnoticeable, to mild, to severe.
- Bed bugs feed during your most vunerable time-sleep. Because you are unlikely to see the bed bugs, the bites may go unnoticed or be mistaken for another type of bite or reaction.
- Bed bugs are known to harbor 28 different human pathogens, however transmission of these diseases to people via bed bug bites has not been confirmed scientifically.
- Some individuals repond to bed bug infestations with anxiety, stress, and insomnia, while others are upset to the point that their lives are completely unmanageable.
- Visible symptoms vary from person to person.
- Bed bug bites can take from immediate to four weeks to display symptoms.
- Scientists believes that up to 70% of the population do not react to bed bug bites.
Where Do Bed Bugs Hide?
- Bed frame and box spring.
- Tufts, seams, and folds of mattresses.
- Dresser drawers, wall units, end tables, closets.
- Couches, tables, and chairs.
- Cracks and crevices in hardwood flooring.
- Under carpets, between walls, behind wallpaper, and under tack strips.
- Baseboards, window and door frames, picture frames.
- Electrical plug outlets and switches.
- Lamps, telephones, electronics, televisions, computers, radios, and alarm clocks.
- Suitcases, luggage, backpacks, purses, footwear, clothing, and jackets.
- Book bindings, magazines, CDs, and DVD's.
- Bed bugs prefer fabric, wood, and paper.
- Bed bugs can hide in cracks smaller than 1mm.